The cumulative distribution function
Last updated on 2024-03-12 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- What is the empirical cumulative distribution function?
Objectives
- Demonstrate the cumulative distribution function with an example.
The cumulative distribution is the integral of the distribution, and
thus the empirical cumulative distribution is the integral of the
histogram. It gives you the percentage of values that are smaller than a
certain value.
We can visualize it with stat_ecdf in
ggplot2.
R
data.frame(frog_sizes) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=frog_sizes))+
stat_ecdf()
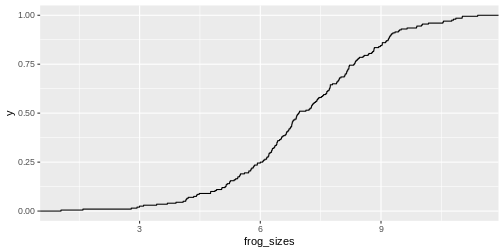
As for the histogram, you could calculate the expected values for the cumulative distribution and add them to the plot:
R
sizes <- seq(0,14,.5)
theoretical_cdf <- pnorm(sizes, mean=7, sd=2)
data.frame(frog_sizes) %>%
ggplot(aes(frog_sizes)) +
stat_ecdf()+
geom_line(data=data.frame(sizes,theoretical_cdf), aes(sizes, theoretical_cdf),colour="green")
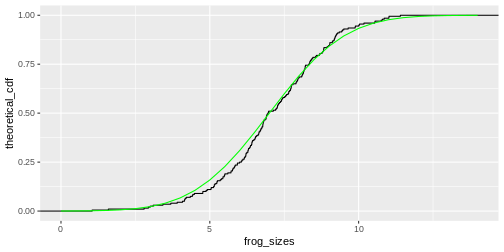
Off this plot you can read for a frog size of \(x\) (e.g. 7cm), that about 50% of the values are smaller than this value. So this is really just another way to display the histogram.
